A Brief History of Rowing Machines
The history of rowing machines begins earlier than many people think. In fact, at the end of the 19th century, there were a few indoor rowers already patented and in use for exercise and a sort of rudimentary training for individuals who routinely rowed outdoors in good weather. The first one widely used was a hydraulic model patented in 1872 by W.B. Curtis.
19th Century Rowing Machines
As the turn of the century rolled around, these first models were very basic, didn’t have a particularly fluid movement and didn’t really emulate the motion of actual rowing. They were, however, the only options available and throughout the first half of the twentieth century, these rowing machines remained in use despite the extremely heavy flywheels and the machines’ choppy movement.
A mechanical braking system was put into use on most of these rowers. As the history of rowing machines marched on, pneumatic resistance continued to remain popular, but there was still no accurate way to gauge the effectiveness or resistance of a workout.
1900 – 1960, Rowing Machines On College Campuses

Between about 1900 and the middle of the century, the Narragansett Machine Company in Providence, Rhode Island began producing indoor rowers that were sturdy and reliable. These soon made their way onto college campuses, where rowing crews used them for off season training.
In some areas, the machines were even packed up and carted with the team for training purposes, despite their hefty weight and cumbersome design.
A major development in the history of rowing machines was the development of a simple ergometer in the 1970s by Gjessing-Nilson. This Norwegian ergometer used a friction braking system and industrial straps over the rim of the flywheel.
Weights were attached to the strap, allowing users to calculate the amount of friction produced. A leather cord hanging from the handlebars ran over a pulley so that users could adjust the gear and speed. Although rudimentary, this machine was considered the best available and the most accurate at the time.
Indoor Rowing Comes of Age
In the 1980s, indoor rowers began to show a variety of refinements in design. Air resistance technology was a major innovation utilizing a new braking system with the traditional flywheel design of the earlier decades. The flywheels, however, became increasingly lighter as new and better materials were used, including stainless steel, wood and aluminum. This phased out the older, iron flywheels.
In 1982, some college students began an informal competition between rowers using the indoor machines available in the gym. The history of rowing machines took a sharp turn when these competitions soon spread across the country and resulted in today’s World Indoor Rowing Championships.
Air resistance ergometers were also developed in the 1980s. These ergometers could accurately measure any workout and contributed to the increased popularity of rowing machines for use as training equipment for watercraft competitors and serious fitness buffs. Continued improvements brought both rowing machines and ergometers into the twenty-first century.
In 1988, Casper Rekers, a Dutch engineer, developed the latest innovation in rowing machines in what he called a rowing “simulator,” which used a resistance tool mounted on bearings alongside the bar that carried the rower so that movement was aligned with the rower’s actual mass. This gives the most realistic movement yet and virtually eliminates tension on the joints.
The History of Rowing Machines Continues to Evolve
Today there are multiple manufacturers who produce dozens of rowing machines for both commercial and in-home use. While some of these still use hydraulic or pneumatic resistance, the majority now use air, magnetic or water resistance.
Each of these models has advantages and disadvantages, making some more popular with home users while others continue to capture the market for commercial or training use.
As the history of rowing machines continues to advance moving through the twenty-first century, they will no doubt continue to improve so that users can get the most efficient workout possible.
UPDATE: March Rowing Machine Sales are going strong!
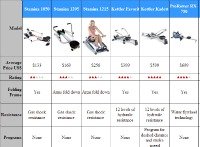
Our Expert's Best Rowers For 2026
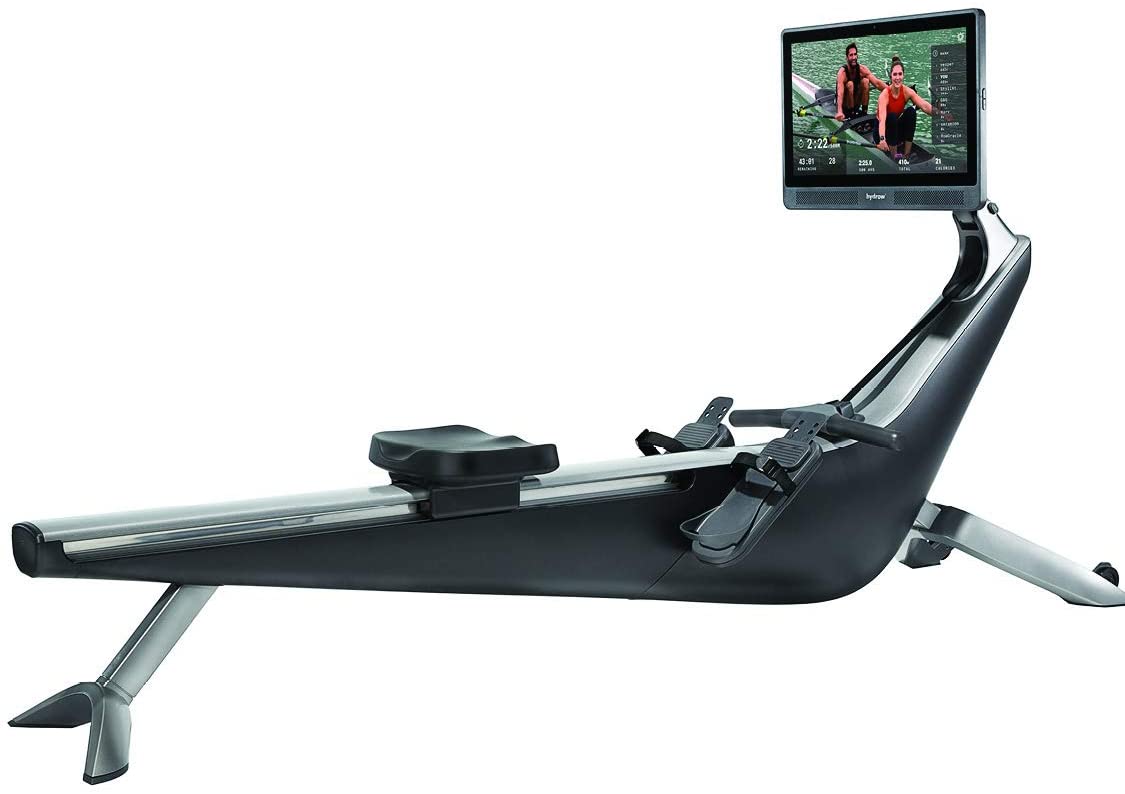
OVERALL WINNER
An incredible rowing machine with innovative technology and unique live and on-demand workouts.
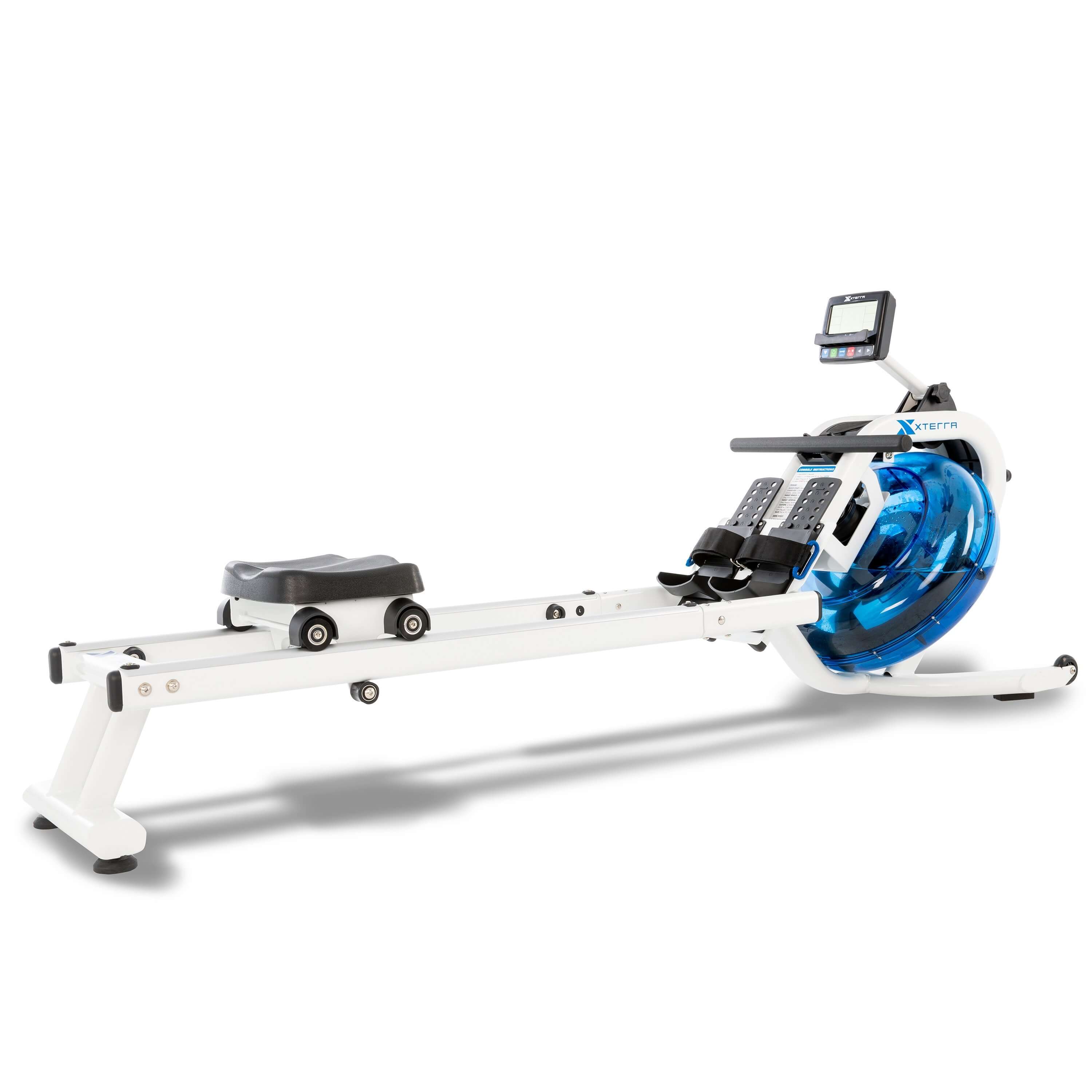
BEST WATER ROWER
The XTERRA ERG 650W rowing machine is a stunning piece of fitness equipment and offers an amazing simulation of the feel of on-the-water rowing.
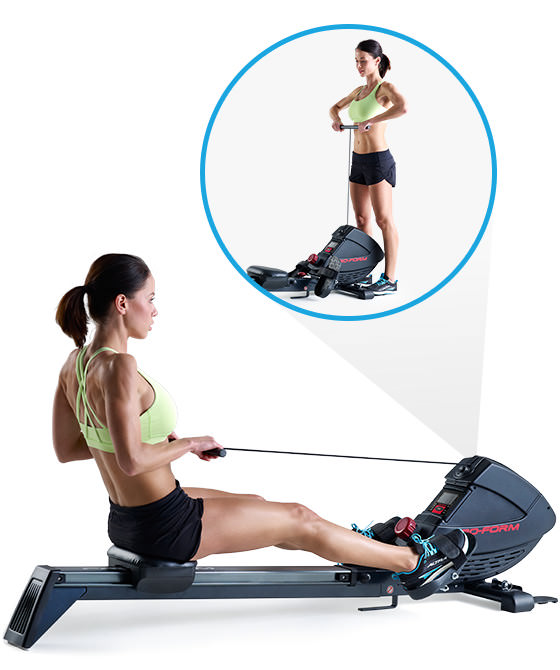
BEST BUDGET ROWER
A solid budget model offering great value for the money, with continuous resistance and ergonomic design.
OTHER PRICE RANGES